The Challenger Strategy Behind Back Markets Growth

Market Challenger Strategies вђ How To Attack To Increase Market Share Market challenger strategies, in simplest words, are the marketing strategies that a firm adopts to challenge or attack the market leader or immediate competitors to earn projected revenue and capture market share. that firm can be either new in the market or holds a runner up, third, or even lower position in the competition. A flanking strategy identifies shifts in the market that create gaps and develops strategies to fill those gaps. it means attacking the competitor on its weak points. here, the market challenger determines the competitor’s weak areas in terms of two strategic dimensions, i.e., geographic and segmental, and then pushes its product in that area.

What Are Market Challenger Strategies Definition And Meaning 2) flank attack. the above example of pepsi and coke contains 2 brands which are very strong in the fmcg market and have no other competitor. thus, they use frontal attacks. but what if a small player has to take on a mammoth. then the player uses a flank attack and attacks the competition based on its weaknesses. Attack strategies are proactive and aggressive approaches taken against a particular competitor to achieve market dominance. often the competitor being challenged is the market leader and the company doing the attacking is a looking to take market share from them. attack strategies are usually led by marketing teams and regarded as a type of. A market challenger is a firm that has a market share below that of the market leader, but enough of a presence that it can exert upward pressure in its effort to gain more control. Frontal attack: this is where the challenger measures everything against its competitors (price, distribution, and product). generally, the company or brand with the largest resources wins. flank attack: this is where the challenge looks to see the gaps that the market leader might be missing. blitz attack: this is where the challenger.
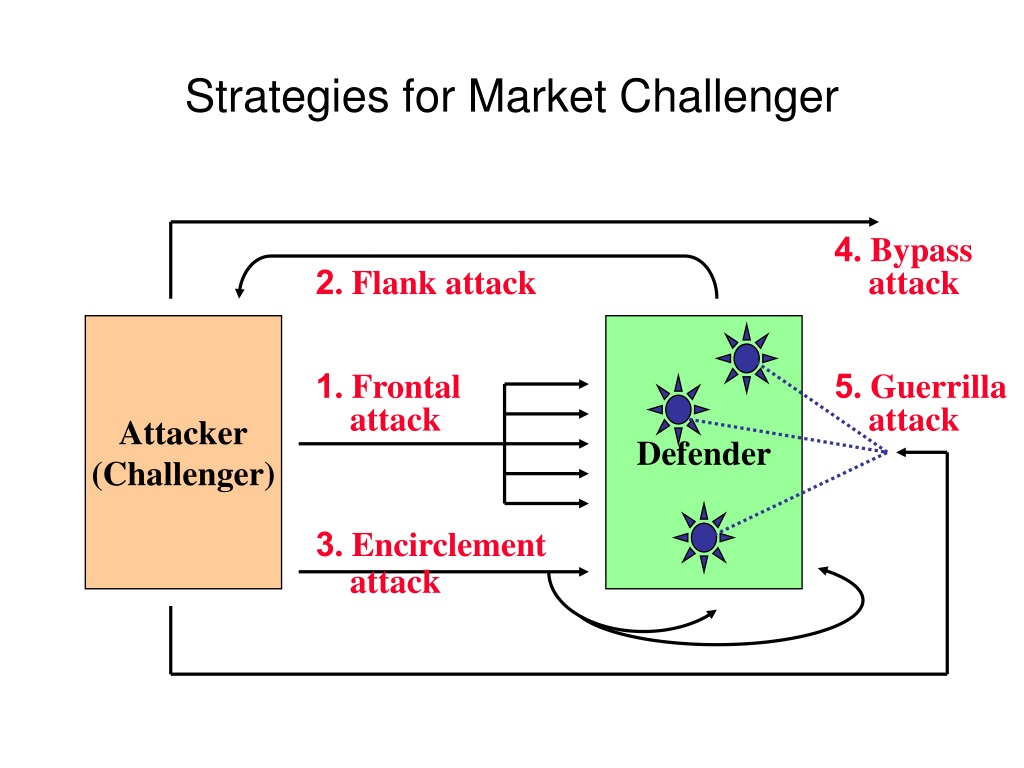
Ppt Analysis Of Competition Powerpoint Presentation Free Download A market challenger is a firm that has a market share below that of the market leader, but enough of a presence that it can exert upward pressure in its effort to gain more control. Frontal attack: this is where the challenger measures everything against its competitors (price, distribution, and product). generally, the company or brand with the largest resources wins. flank attack: this is where the challenge looks to see the gaps that the market leader might be missing. blitz attack: this is where the challenger. Agility: the market challenger’s core competency. alongside the right talent, market challengers must possess agility: the ability to operate at multiple speeds and the capacity to evolve. many enterprises’ deep rooted technological, compliance and architectural constraints — the very attributes that helped them win in the old economy. The theory behind the approach is that, by challenging the customer’s thought process, salespeople can convert more leads into long term customers. to achieve this, the challenger sales model relies on insight selling, which involves providing unique insights and data to your prospects to help them see the value in your product or service.

Market Challenger Strategies Meaning Examples Pros Cons Agility: the market challenger’s core competency. alongside the right talent, market challengers must possess agility: the ability to operate at multiple speeds and the capacity to evolve. many enterprises’ deep rooted technological, compliance and architectural constraints — the very attributes that helped them win in the old economy. The theory behind the approach is that, by challenging the customer’s thought process, salespeople can convert more leads into long term customers. to achieve this, the challenger sales model relies on insight selling, which involves providing unique insights and data to your prospects to help them see the value in your product or service.

Comments are closed.