The Four Shock Factors

Different Types Of Shock And Therapeutive Interventions Ppe Medical Like water and metal, the human body is a conductor of electricity. therefore, it’s important to avoid situations where you might come into contact with elec. The four types of shock include distributive shock, cardiogenic shock, hypovolemic shock (hypovolemia), and obstructive shock. shock is a multisystem phenomenon that disrupts the body’s physiology and causes reduced tissue perfusion (oxygenation). physiological shocks are classified into four main categories: distributive shock. cardiogenic.

The Four Shock Factors Youtube The four types of shock are hypovolemic, distributive, cardiogenic, and obstructive. subtypes of distributive shock include septic shock, anaphylactic shock, and neurogenic shock. causes include blood loss, fluid loss, allergic reaction, systemic reaction to infection, spinal cord injury, heart attack, heart failure, and pressure around the. The four types of shock are hypovolemic shock (caused by severe blood or fluid loss), distributive shock (resulting from widespread vasodilation and decreased peripheral vascular resistance, such as in septic shock), cardiogenic shock (due to heart failure resulting in inadequate cardiac output), and obstructive shock (caused by mechanical. Shock is a life threatening manifestation of circulatory failure. circulatory shock leads to cellular and tissue hypoxia resulting in cellular death and dysfunction of vital organs. effects of shock are reversible in the early stages, and a delay in diagnosis and or timely initiation of treatment can lead to irreversible changes, including multiorgan failure (mof) and death. Shock results from four potential, and not necessarily exclusive, pathophysiological mechanisms 3: hypovolemia (from internal or external fluid loss), cardiogenic factors (e.g., acute myocardial.
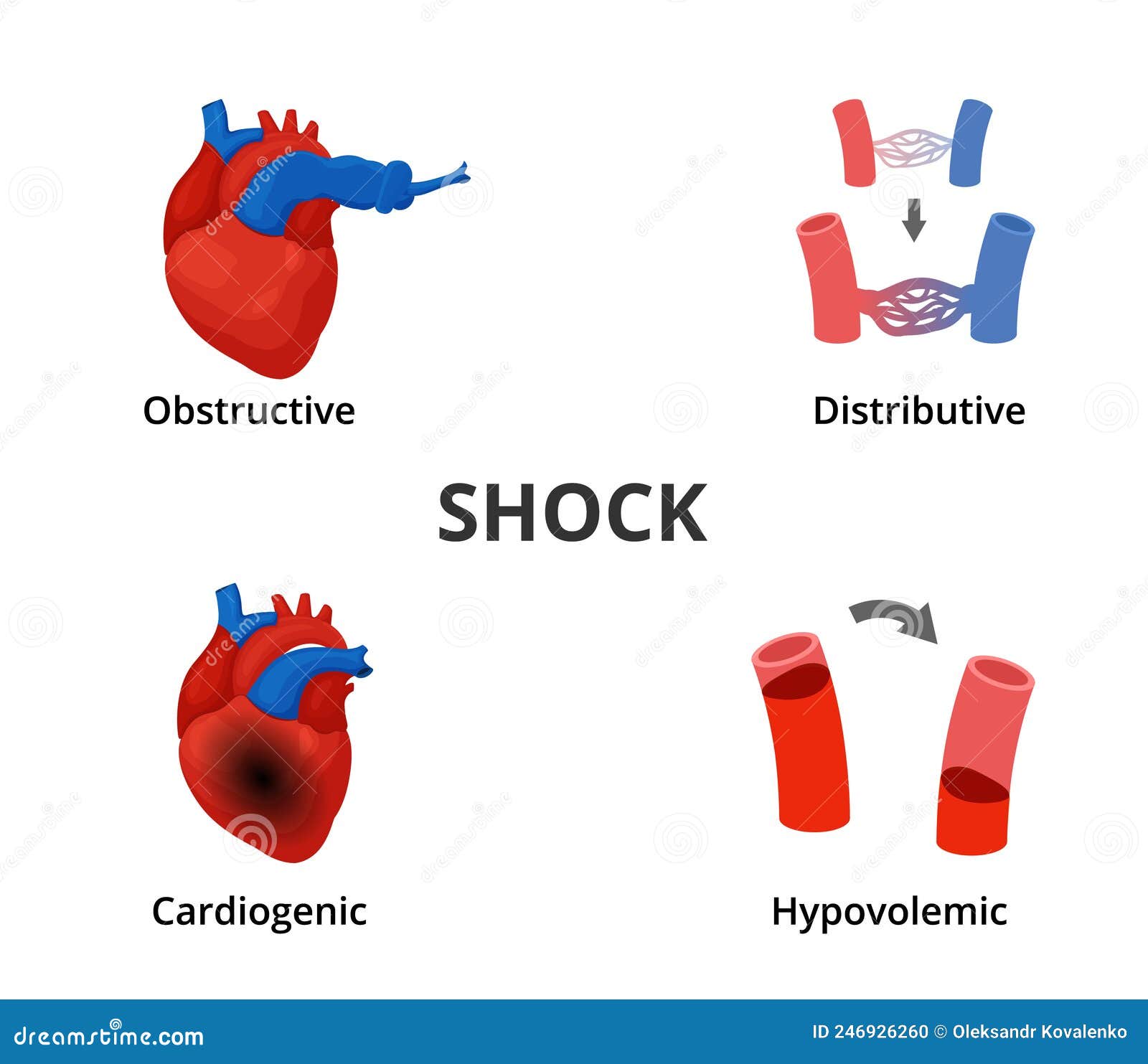
4 Types Of Shock Diagram Medical Emergency Infographics Stock Vector Shock is a life threatening manifestation of circulatory failure. circulatory shock leads to cellular and tissue hypoxia resulting in cellular death and dysfunction of vital organs. effects of shock are reversible in the early stages, and a delay in diagnosis and or timely initiation of treatment can lead to irreversible changes, including multiorgan failure (mof) and death. Shock results from four potential, and not necessarily exclusive, pathophysiological mechanisms 3: hypovolemia (from internal or external fluid loss), cardiogenic factors (e.g., acute myocardial. The four types of shock. there are four types of shock. the first three states of shock are caused by decreased cardiac output. risk factors. shock can occur from trauma and other incidents. What causes shock? there are four types of shock depending on the underlying cause: hypovolemic; cardiogenic; obstructive; and distributive, which encompasses anaphylactic, septic, and neurogenic shock. hypovolemic shock occurs as a result of a decrease in intravascular volume, which can be caused by severe bleeding, fluid losses from vomiting.

5 Common Causes Of Electrical Shocks At Home Same Day Pros The four types of shock. there are four types of shock. the first three states of shock are caused by decreased cardiac output. risk factors. shock can occur from trauma and other incidents. What causes shock? there are four types of shock depending on the underlying cause: hypovolemic; cardiogenic; obstructive; and distributive, which encompasses anaphylactic, septic, and neurogenic shock. hypovolemic shock occurs as a result of a decrease in intravascular volume, which can be caused by severe bleeding, fluid losses from vomiting.

Comments are closed.