The Multiplier Effect In Less Than 5 Minutes

The Multiplier Effect In Less Than 5 Minutes Youtube Explainer video of the economic concept "the multiplier". The multiplier effect refers to the proportional amount of increase, or decrease, in final income that results from an injection, or withdrawal, of capital. the multiplier effect measures the.

Multiplier Effect Definition Economics Formula Example In economics, the multiplier effect happens when the change in a particular economic input (e.g. government spending) causes a larger change in an economic output (e.g. gross domestic product). the multiplier effect was first theorized by economist paul samuelson in his paper “ the relation of home investment to unemployment ” (1931). The multiplier effect. the multiplier effect is defined as the change in income to the permanent change in the flow of expenditure that caused it. in other words, the multiplier effect refers to the increase in final income arising from any new injections. injections are additions to the economy through government spending, money from exports. The multiplier effect arises because one agent’s spending is another agent’s income. when a spending project creates new jobs for example, this creates extra injections of income and demand into a country’s circular flow. the negative multiplier effect occurs when an initial withdrawal or leakage of spending from the circular flow leads. The multiplier effect is also visible on the keynesian cross diagram. figure b.11 shows the example we have been discussing: a recessionary gap with an equilibrium of $700, potential gdp of $800, the slope of the aggregate expenditure function (ae 0) determined by the assumptions that taxes are 30% of income, savings are 0.1 of after tax income, and imports are 0.1 of before tax income.
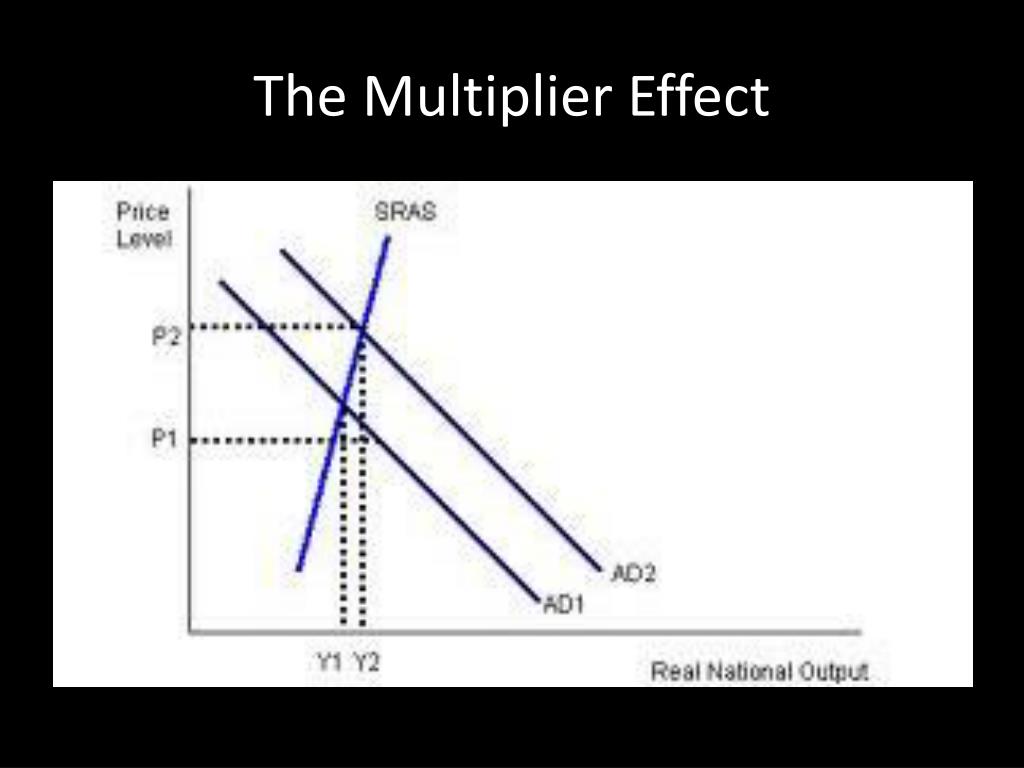
Ppt The Multiplier Effect Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id The multiplier effect arises because one agent’s spending is another agent’s income. when a spending project creates new jobs for example, this creates extra injections of income and demand into a country’s circular flow. the negative multiplier effect occurs when an initial withdrawal or leakage of spending from the circular flow leads. The multiplier effect is also visible on the keynesian cross diagram. figure b.11 shows the example we have been discussing: a recessionary gap with an equilibrium of $700, potential gdp of $800, the slope of the aggregate expenditure function (ae 0) determined by the assumptions that taxes are 30% of income, savings are 0.1 of after tax income, and imports are 0.1 of before tax income. The multiplier effect – definition. the multiplier effect indicates that an injection of new spending (exports, government spending or investment) can lead to a larger increase in final national income (gdp). this is because a proportion of the injection of new spending will itself be spent, creating income for other firms and individuals. Suppose the mpc = 90%; then the mps = 10%. therefore, the spending multiplier is: in this simple case, a change in spending of $100 multiplied by the spending multiplier of 10 is equal to a change in gdp of $1,000. watch the selected clip from this video (stopping at 3:14) for more practice in solving for the spending multiplier.

Comments are closed.