The Routing Table 3 5 Cisco Networking Academy S Introduction To

The Routing Table 3 5 Cisco Networking Academy S Understanding the structure of the routing table will help you verify and troubleshoot routing issues because you will understand the routing table lookup process. routing table terms (3.5.2.1) a dynamically built routing table provides a great deal of information, as shown in figure 3 55. therefore, it is crucial to understand the output. Now that we’ve listed the components of a routing table entry, let’s dive into understanding an entry based on an example. we’ll use the routing table given previously. looking at the first entry below, suppose pc1 would like to send a packet to pc3 on the destination at 101.25.67.0. however, pc3 is not on pc1’s network, so pc1 forwards.

The Routing Table 3 5 Cisco Networking Academy S What is different between ipv6 routing table entries and ipv4 routing table entries? by design ipv6 is classless, so all routes are effectively level 1 ultimate routes. unlike ipv4, ipv6 does not use static routes to populate the routing table. ipv6 routing tables include local route entries, which ipv4 routing tables do not. Cisco networking academy's introduction to routing dynamically. this chapter explains multiple routing protocols (particularly dynamic routing protocols) and describes their relative strengths and weaknesses. it also shows how to read a routing table easily and interpret the ipv6 routing information listed within it. Dynamic versus static routing (3.1.2) routing tables can contain directly connected, manually configured static routes and routes learned dynamically using a routing protocol. Introduction (3.0.1.1) 129 dynamic routing protocols (3.1) 130 dynamic routing protocol overview (3.1.1) 130 dynamic routing protocol evolution (3.1.1.1) 130 dynamic routing protocol components (3.1.1.2) 132 dynamic versus static routing (3.1.2) 133 static routing uses (3.1.2.1) 133 static routing advantages and disadvantages (3.1.2.2) 134.
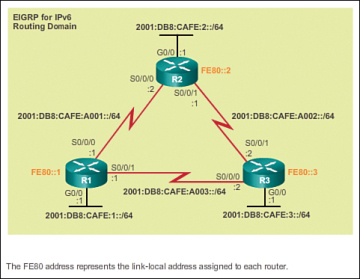
The Routing Table 3 5 Cisco Networking Academy S Dynamic versus static routing (3.1.2) routing tables can contain directly connected, manually configured static routes and routes learned dynamically using a routing protocol. Introduction (3.0.1.1) 129 dynamic routing protocols (3.1) 130 dynamic routing protocol overview (3.1.1) 130 dynamic routing protocol evolution (3.1.1.1) 130 dynamic routing protocol components (3.1.1.2) 132 dynamic versus static routing (3.1.2) 133 static routing uses (3.1.2.1) 133 static routing advantages and disadvantages (3.1.2.2) 134. Types of routing protocols (3.1.4) table 3 1 showed how routing protocols can be classified according to various characteristics. this section gives an overview of the most common ip routing protocols. most of these routing protocols will be examined in detail in other chapters. for now, this section gives a very brief overview of each protocol. A routing table is a repository of all the routes to all the destinations in use by a network. routing tables can be created manually and "learned" by software as it observes network traffic, or they can be built according to routing protocols. a simple print job may be transmitted using static routing, where the host plugs in a previously used.

Comments are closed.