The Threat Of Chronic Wasting Disease In Wisconsin
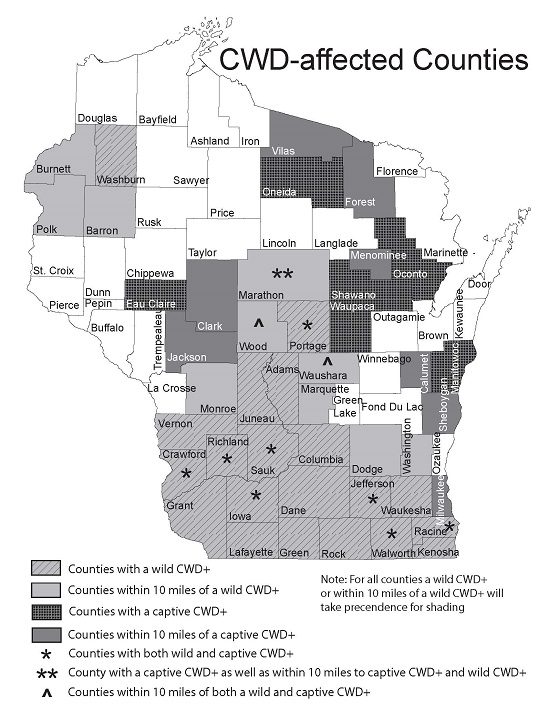
The Murky Status Of Chronic Wasting Disease In Wisconsin Wiscontext Chronic wasting disease is a fatal, infectious nervous system disease of deer, moose, elk and reindeer caribou. it belongs to the family of diseases known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (tses) or prion diseases. cwd occurs only in members of the cervid or deer family both wild and captive. the wisconsin dnr began monitoring the. As of 2017, the wisconsin dnr has classified 44 counties in the state as affected by cwd. while cwd is a growing threat to the health of wisconsin's deer population, scientists are still getting their heads around its potential danger to humans. some prion diseases like creutzfeldt–jakob disease and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (better.
April 27 2018 Wisconsin S Chronic Wasting Disease Issue Downright Scary Deadly deer disease expected to grow rapidly and spread in wisconsin. new science can predict the expansion of biological threats. by communications and publishing april 18, 2017. a new tool, which predicted the recent, rapid growth and continued spread of chronic wasting disease in deer, can help forecast and manage other costly biological. Prevalence is the proportion or percentage of a population that tests positive for a disease. chronic wasting disease (cwd) prevalence depends on the deer's location, sex and age. since testing is done regionally, results can't be used to estimate the statewide prevalence. analyses of the geographic distribution of disease show that the disease. Chronic wasting disease is distinctly different from the other tses, and unlike bse, it never has been linked epidemiologically to human neurological disease. furthermore, cwd never has been demonstrated to infect species other than white tailed deer, mule deer, and elk under natural conditions. the origin of chronic wasting disease (cwd) is. The threat of chronic wasting disease to wisconsin's booming whitetail deer herd is motivating efforts to track and research its spread, but this deadly ailment also imperils efforts to reintroduce wild elk to the state.

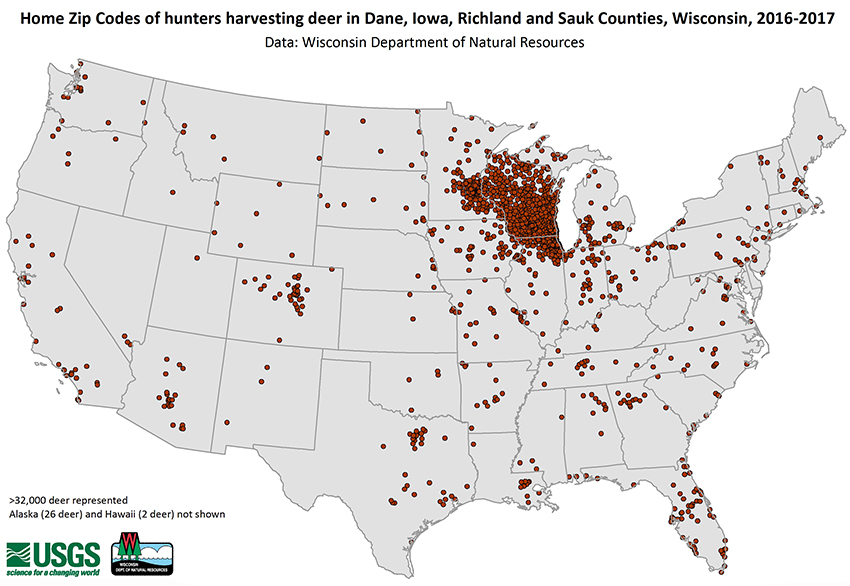
Chronic Wasting Disease Cwd Wisconsin Dnr Chronic wasting disease is distinctly different from the other tses, and unlike bse, it never has been linked epidemiologically to human neurological disease. furthermore, cwd never has been demonstrated to infect species other than white tailed deer, mule deer, and elk under natural conditions. the origin of chronic wasting disease (cwd) is. The threat of chronic wasting disease to wisconsin's booming whitetail deer herd is motivating efforts to track and research its spread, but this deadly ailment also imperils efforts to reintroduce wild elk to the state. The deer herd at the heart of wisconsin's beloved hunting tradition faces a growing threat in the form of chronic wasting disease, caused by an infectious type of protein called prions. the wisconsin department of natural resources began testing for cwd in 1999, detecting more than 100,000 infected deer since, mostly in southern areas of the state. as dnr policies for monitoring cwd shift amid. Chronic wasting disease (cwd) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease affecting free ranging and captive cervids that now occurs in 24 u.s. states and two canadian provinces. despite the potential threat of cwd to deer populations, little is known about the rates of infection and mortality caused by this disease.

Comments are closed.