Time Series Exploration Using R Time Series Data Pattern
Time Series Analysis In R Part 2 Time Series Transformations Date and date time objects. r has two primary types of date classes: date: this puts dates into the format yyy m d and it tracks the number of days since the default of 1970 01 01. datetime: uses the iso 8601 international standard format of yyy m d h:m:s to track the time since 1970 01 01 utc. there are two options for this class:. #timeseriesanalysis #timeseries #forecastingdata code files: github hakeemrehman forecasting using r.
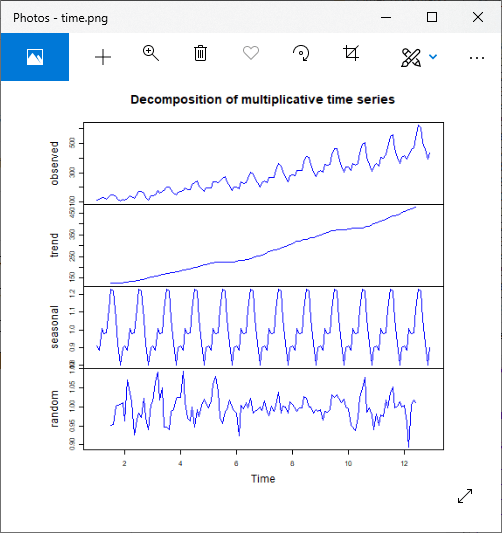
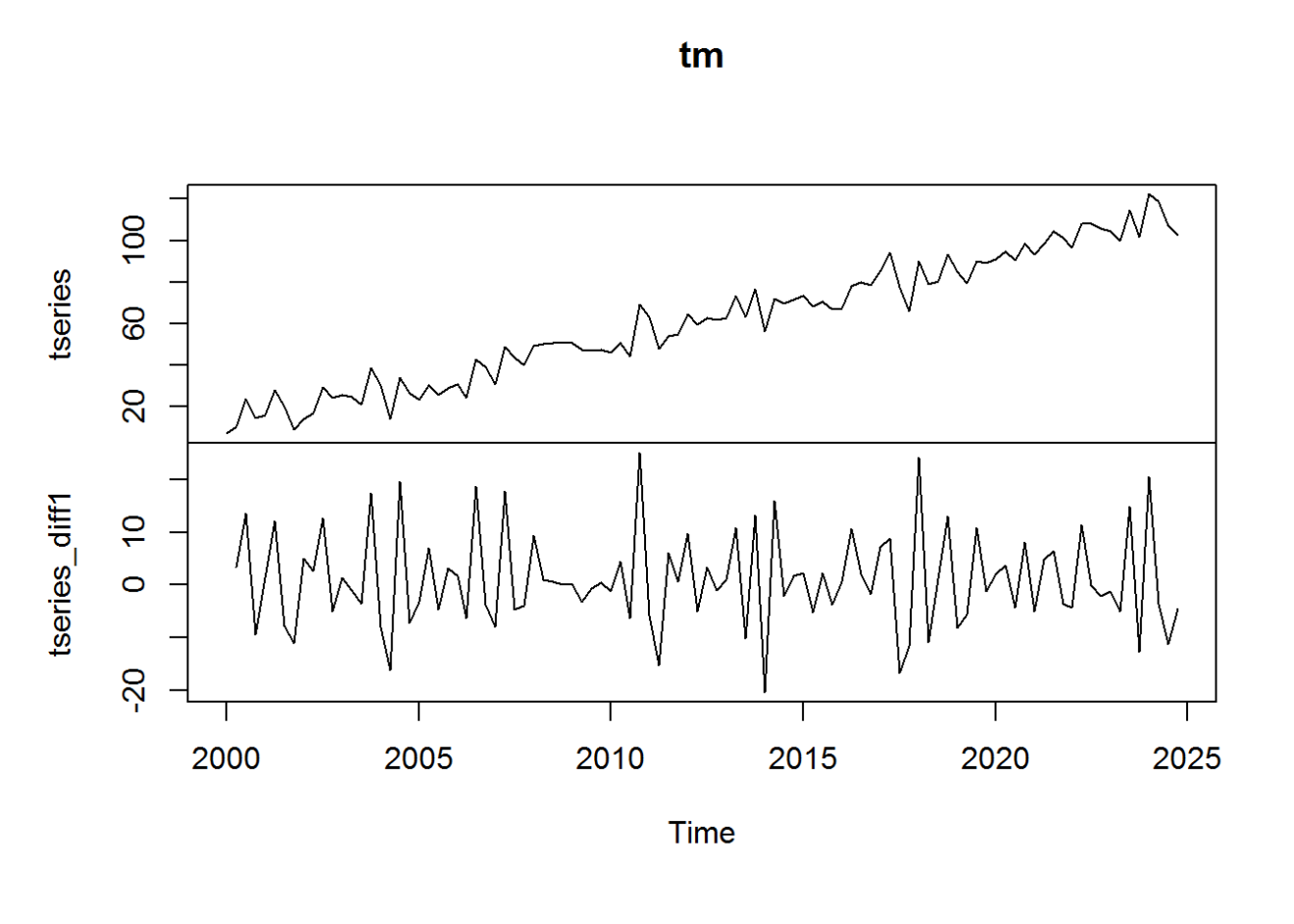
R Time Series Analysis Javatpoint For example, the fpp2::arrivals data set has time series data for “quarterly international arrivals (in thousands) to australia from japan, new zealand, uk and the us. 1981q1 2012q3.” so this time series data has two variables (over and above the time stamp data) (1) arrivals in thousands and (2) country. For most time series patterns, 1 or 2 differencing is necessary to make it a stationary series. but if the time series appears to be seasonal, a better approach is to difference with respective season’s data points to remove seasonal effect. Learn time series analysis with r along with using a package in r for forecasting to fit the real time series to match the optimal model. time series is the measure, or it is a metric which is measured over the regular time is called as time series. time series analysis example are financial, stock prices, weather data, utility studies and many. To store the data in a time series object, we use the ts () function in r. for example, to store the data in the variable ‘kings’ as a time series object in r, we type: > kingstimeseries < ts (kings) > kingstimeseries. time series: start = 1. end = 42.

Comments are closed.