Trig 1 11 Trigonometric Ratios Of Special Right Triangles Part 1

Trig 1 11 Trigonometric Ratios Of Special Right Triangles Part 1 Youtube Hypotenuse equals twice the smallest leg, while the larger leg is 3–√ 3 times the smallest. one of the two special right triangles is called a 30 60 90 triangle, after its three angles. 30 60 90 theorem: if a triangle has angle measures 30∘ 30 ∘, 60∘ 60 ∘ and 90∘ 90 ∘, then the sides are in the ratio x: x 3–√: 2x x: x 3: 2 x. The cotangent function: cot(θ) = x y cot (θ) = x y. example 1.2.1 1.2. 1. the point (3, 4) is on the circle of radius 5 at some angle θ θ. find the six trigonometric function values of θ θ. solution. we have x = 3 x = 3, y = 4 y = 4, and r = 5 r = 5. using the previously listed definitions we have.

Special Triangles Trig Ratios вђў 2 1c Pre Calculus 11 Youtube Pythagorean’s theorem. 2 2 = 2. example 1: in right triangle. with the right angle find. if. = 4√5 and = 4. two special triangles are 30° − 60° − 90° triangles and 45° − 45° − 90° triangles. in such triangles, sides are proportional. you need to know the length of one side only to find the remaining sides. How to evaluate trig functions of special angles? easy way to use right triangle and label sides to find sin, cos, tan, cot, csc, and sec of the special angles, and of angles at multiples of 90°. this is part 1. scroll down the page for part 2. example: find cos 90, tan 90, sin 630, sin 135, tan ( 405), sin 210, tan ( 30). show video lesson. Make a table with the side ratios and the information given, then write equations and solve for the missing side lengths. 18 = x√3 18 √3 = x x = 18√3 = 18√3 ⋅ √3 √3 = 18√3 3 = 6√3 x = 6√3. note that you need to rationalize denominators. now use the calculated x value to solve for 2x. 2x = 2(6√3) 2x = 12√3. If we ignore the height of the person, we solve the following triangle: figure 1.4.10. given the angle of depression is 53 ∘, ∠a in the figure above is 37 ∘. we can use the tangent function to find the distance from the building to the park: tan37 ∘ = opposite adjacent = d 100 tan37 ∘ = d 100 d = 100tan37 ∘ ≈ 75.36 ft.
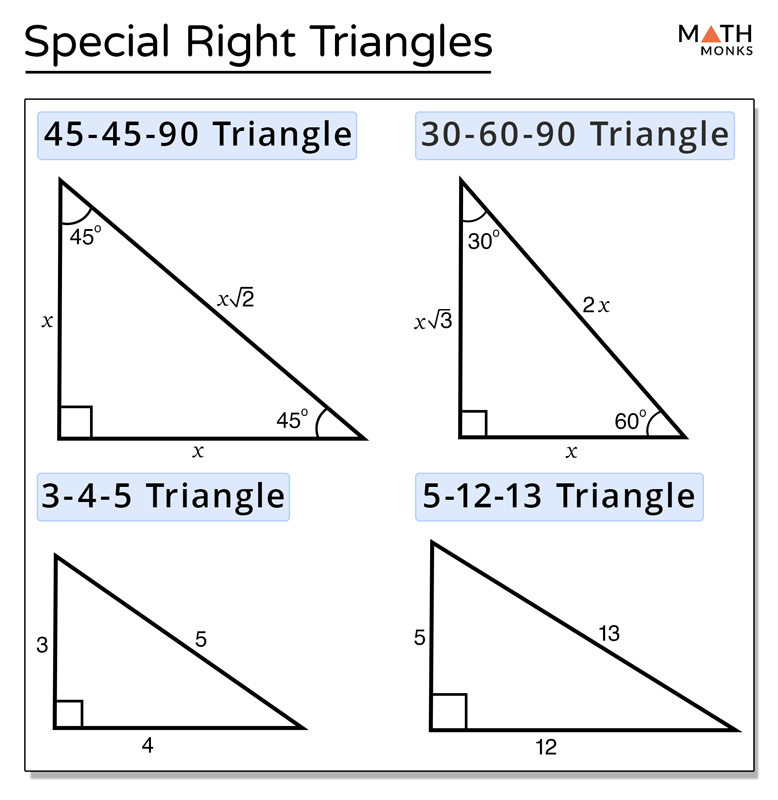
Special Right Triangles вђ Definition Formula Examples Make a table with the side ratios and the information given, then write equations and solve for the missing side lengths. 18 = x√3 18 √3 = x x = 18√3 = 18√3 ⋅ √3 √3 = 18√3 3 = 6√3 x = 6√3. note that you need to rationalize denominators. now use the calculated x value to solve for 2x. 2x = 2(6√3) 2x = 12√3. If we ignore the height of the person, we solve the following triangle: figure 1.4.10. given the angle of depression is 53 ∘, ∠a in the figure above is 37 ∘. we can use the tangent function to find the distance from the building to the park: tan37 ∘ = opposite adjacent = d 100 tan37 ∘ = d 100 d = 100tan37 ∘ ≈ 75.36 ft. Small (across from 30 degrees) 45 45 90: if you know the hypotenuse, do this to find the legs: divide by √2. 30 60 90 right triangle. type of triangle formed when an altitude is drawn in an equilateral triangle. 30 60 90: to find the medium leg do this to the small leg: multiply by √3. 30 60 90: to find the small leg do this to the medium. Right triangle trigonometry special right triangles examples find x and y by using the theorem above. write answers in simplest radical form. 1. solution: the length of the shorter leg is 6. since the length of the hypotenuse is twice the length of the shorter leg, x =2 6 12.⋅= the length of the longer leg is 3 times.

Special Right Triangles Worksheet Small (across from 30 degrees) 45 45 90: if you know the hypotenuse, do this to find the legs: divide by √2. 30 60 90 right triangle. type of triangle formed when an altitude is drawn in an equilateral triangle. 30 60 90: to find the medium leg do this to the small leg: multiply by √3. 30 60 90: to find the small leg do this to the medium. Right triangle trigonometry special right triangles examples find x and y by using the theorem above. write answers in simplest radical form. 1. solution: the length of the shorter leg is 6. since the length of the hypotenuse is twice the length of the shorter leg, x =2 6 12.⋅= the length of the longer leg is 3 times.

Comments are closed.