Truss Method Of Joints In 6 Minutes

Truss Analysis By Method Of Joints Worked Example 1 Youtube I default tensile rule.ii which joint to check first.iii force direction.please pause when required. Lecture explaining the method of joints, method of sections, and zero force members.0:00 truss definition0:20 truss assumptions2:22 method of joints3:35 forc.

Method Of Joints Truss Step 1: calculate the reactions at the supports. first, we calculate the reactions at the supports. we will start by looking at a simple example of a 5 member truss system: to calculate the bending moment in this truss system, we first take the sum of moments at the left reaction to be zero. we do this by ignoring all the members and just. Using the method of sections and method of joints to work out the internal forces in statically determinate trusses. by dr seán carroll. in this tutorial we’re going to focus on trusses, also known as pin jointed structures. we’ll discuss their strengths and the common methods of manual truss analysis. we’re going to start at the very. Figure 5.4.1: the first step in the method of joints is to label each joint and each member. treating the entire truss structure as a rigid body, draw a free body diagram, write out the equilibrium equations, and solve for the external reacting forces acting on the truss structure. this analysis should not differ from the analysis of a single. Step 1: examples of trusses. trusses are used in the construction of nearly every road bridge you will encounter in your city's highway system. the 3 main types of trusses used in bridge design are pratt, warren and howe. truss type differs only by the manner and angle in which the members are connected at joints.

Explained Analysis Of Trusses Engineering Mechanics Method Of Figure 5.4.1: the first step in the method of joints is to label each joint and each member. treating the entire truss structure as a rigid body, draw a free body diagram, write out the equilibrium equations, and solve for the external reacting forces acting on the truss structure. this analysis should not differ from the analysis of a single. Step 1: examples of trusses. trusses are used in the construction of nearly every road bridge you will encounter in your city's highway system. the 3 main types of trusses used in bridge design are pratt, warren and howe. truss type differs only by the manner and angle in which the members are connected at joints. The method centers on the joints or connection points between the members, and it is usually the fastest and easiest way to solve for all the unknown forces in a truss structure. using this method: the process used in the method of joints is outlined below: in the beginning it is usually useful to label the members and the joints in your truss. To start the analysis by the method of joints, choose one of the joints on the truss into which two or fewer unknown members frame and also on which some known forces act. joints a and e are the only possibilities, so we choose joint a. the free body diagram of that joint is shown in fig. 3.3 3. figure 3.3 3: joint a.
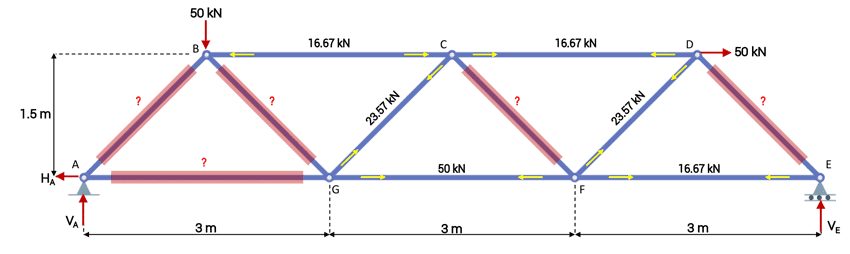
Truss Analysis Tutorial Method Of Joints And Sections Degreetutors The method centers on the joints or connection points between the members, and it is usually the fastest and easiest way to solve for all the unknown forces in a truss structure. using this method: the process used in the method of joints is outlined below: in the beginning it is usually useful to label the members and the joints in your truss. To start the analysis by the method of joints, choose one of the joints on the truss into which two or fewer unknown members frame and also on which some known forces act. joints a and e are the only possibilities, so we choose joint a. the free body diagram of that joint is shown in fig. 3.3 3. figure 3.3 3: joint a.

Comments are closed.