Turbo Intercooler Diagram

Turbo And Intercooler Diagram Turbochargers are centrifugal compressors driven by an exhaust gas turbine and employed in engines to boost the charge air pressure. turbocharger performance. Air to water. as the name suggests, air to water intercoolers use water to lower the temperature of the compressed air. cool water is pumped through the unit, extracting heat from the air as it passes through the unit. as this water heats up, it is then pumped through a radiator or cooling circuit, before re entering the intercooler once cool.

Turbo Intercooler Diagram The lower port is the passenger side turbo air, which has to go up and over the driver side turbo inlet. to do this, we used a 180 degree elbow. see all 24 photos. with the location marked, we cut. Now that you know what the turbo intercooler does, let’s get a better understanding of how the different types of intercooled turbos work. there are two main types: air to air and liquid to air. the main difference between the two is the heat transfer agent they use. air to air intercoolers rely on ambient air to cool down the warm air, while. At its essence, an intercooler is a heat exchanger. in an air to water intercooler, the heat exchange occurs between the air coming in and the water flowing through the intercooler–the heat from your charge pipes is transferred to the water, and cooler and denser air is sent through the other side. one of the key benefits to this type of. Housing inds it way to the turbo’s center housing, raising its temperature. these extreme temperatures in the center housing can result in oil coking. to minimize the effects of heat soak back, water cooled center housings were introduced. these use coolant from the engine to act as a heat sink after engine shutdown, preventing the oil from.
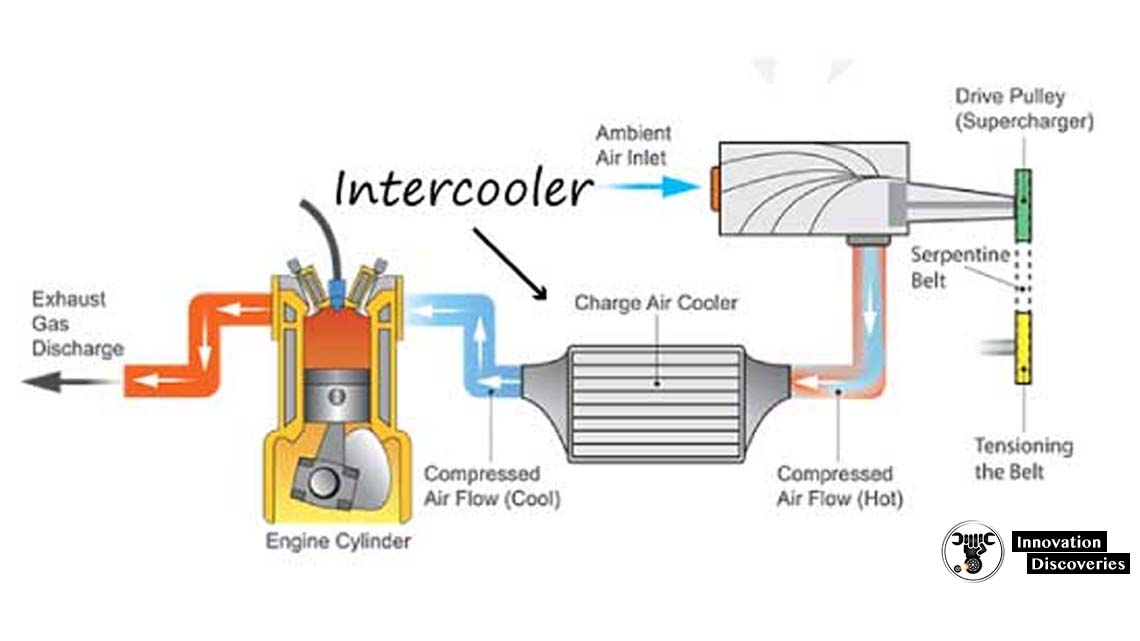
Mechanical World Turbo Intercooler Functions Explained At its essence, an intercooler is a heat exchanger. in an air to water intercooler, the heat exchange occurs between the air coming in and the water flowing through the intercooler–the heat from your charge pipes is transferred to the water, and cooler and denser air is sent through the other side. one of the key benefits to this type of. Housing inds it way to the turbo’s center housing, raising its temperature. these extreme temperatures in the center housing can result in oil coking. to minimize the effects of heat soak back, water cooled center housings were introduced. these use coolant from the engine to act as a heat sink after engine shutdown, preventing the oil from. For instance, if the turbo heats the air charge to 200 degrees, and the intercooler lowers it to 109 degrees, and the ambient air temperature passing over the cooler is 70 degrees, this. An intercooler is basically an air to air radiator. the hot air from the turbo enters at one end, and as cooled as it passes through the intercooler (much like the water in a car’s radiator) before entering the engine at a much lower temperature. this allows the engine to make full use of a simple principal of physics; cooler air is more.

Mechanical World Turbo Intercooler Functions Explained For instance, if the turbo heats the air charge to 200 degrees, and the intercooler lowers it to 109 degrees, and the ambient air temperature passing over the cooler is 70 degrees, this. An intercooler is basically an air to air radiator. the hot air from the turbo enters at one end, and as cooled as it passes through the intercooler (much like the water in a car’s radiator) before entering the engine at a much lower temperature. this allows the engine to make full use of a simple principal of physics; cooler air is more.

Comments are closed.