Understanding Boxplots How To Read And Interpret A Bo Vrogue Co
Understanding Boxplots How To Read And Interpret A Bo Vrogue Co Here’s how to interpret it: minimum (q0): the leftmost line represents the minimum value in the data set that is not an outlier. first quartile (q1): the left edge of the box marks the first. A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. they particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. a box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format. analysts frequently use them during exploratory data analysis because they.
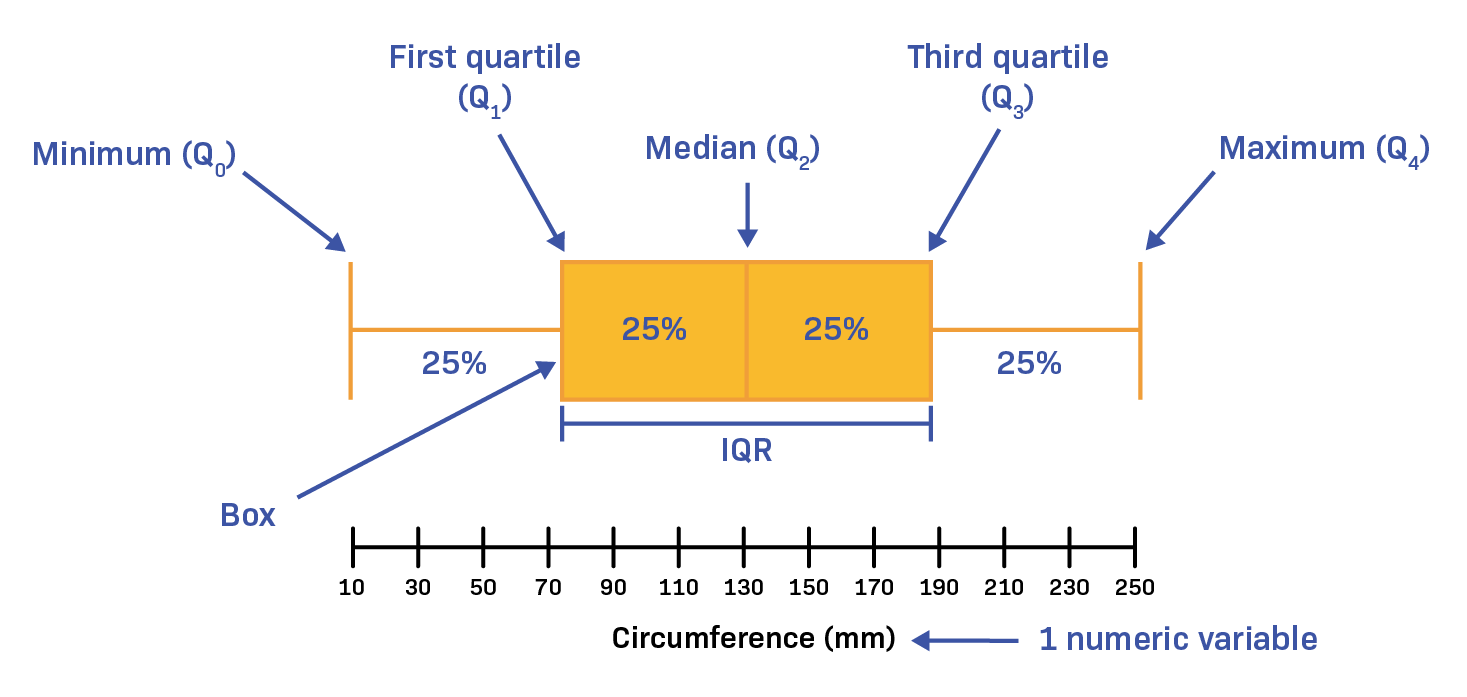
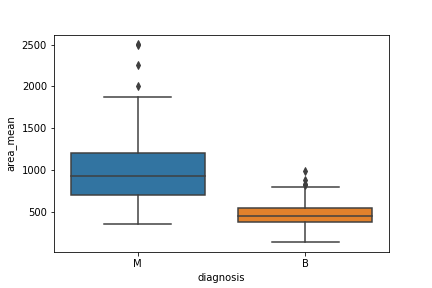
Understanding Boxplots How To Read And Interpret A Bo Vrogue Co A boxplot is a graph that gives a visual indication of how a data set’s 25th percentile, 50th percentile, 75th percentile, minimum, maximum and outlier values are spread out and compare to each other. boxplots are drawn as a box with a line inside of it, and has extended lines attached to each of its sides (known as “whiskers”). Box plots are useful as they provide a visual summary of the data enabling researchers to quickly identify mean values, the dispersion of the data set, and signs of skewness. note that the image above represents data that has a perfect normal distribution , and most box plots will not conform to this symmetry (where each quartile is the same. Box plots are drawn for groups of w@s scale scores. they enable us to study the distributional characteristics of a group of scores as well as the level of the scores. to begin with, scores are sorted. then four equal sized groups are made from the ordered scores. that is, 25% of all scores are placed in each group. Step 3. draw a line inside the box to indicate the position of the median. so far, the lower quartile (q1), the upper quartile (q2) and the median have been constructed, forming the box portion of the box plot. step 4. draw lines to indicate the position of the maximum and minimum and connect these lines to the box.

Understanding Boxplots How To Read And Interpret A Bo Vrogue Co Box plots are drawn for groups of w@s scale scores. they enable us to study the distributional characteristics of a group of scores as well as the level of the scores. to begin with, scores are sorted. then four equal sized groups are made from the ordered scores. that is, 25% of all scores are placed in each group. Step 3. draw a line inside the box to indicate the position of the median. so far, the lower quartile (q1), the upper quartile (q2) and the median have been constructed, forming the box portion of the box plot. step 4. draw lines to indicate the position of the maximum and minimum and connect these lines to the box. Topic. the box and whisker plot is an exploratory graphic, created by john w. tukey, used to show the distribution of a dataset (at a glance). think of the type of data you might use a histogram with, and the box and whisker (or box plot, for short) could probably be useful. the box plot, although very useful, seems to get lost in areas outside. Boxplots, also known as box and whisker plots, are a standard way of displaying data distribution based on a five number summary: minimum, first quartile (q1), median, third quartile (q3), and maximum. boxplots are particularly useful for identifying outliers and understanding the spread and skewness of the data.

Comments are closed.