Understanding Flow Coefficient A Guide For Valve Sizing

Understanding Flow Coefficient A Guide For Valve Sizing 56 Off The following subsections will explain what to know about how valve sizing works. flow coefficient (c v) the flow coefficient is central to valve sizing. it represents the volume of water at 60 °f that can flow through the valve in one minute with a 1 psi pressure drop. a higher c v indicates a higher flow capacity. A valve that is too small will not pass the required flow, and the process will be starved. an oversized valve will be more expensive, and it may lead to instability and other problems. the days of selecting a valve based upon the size of the pipeline are gone. selecting the correct valve size for a given application.
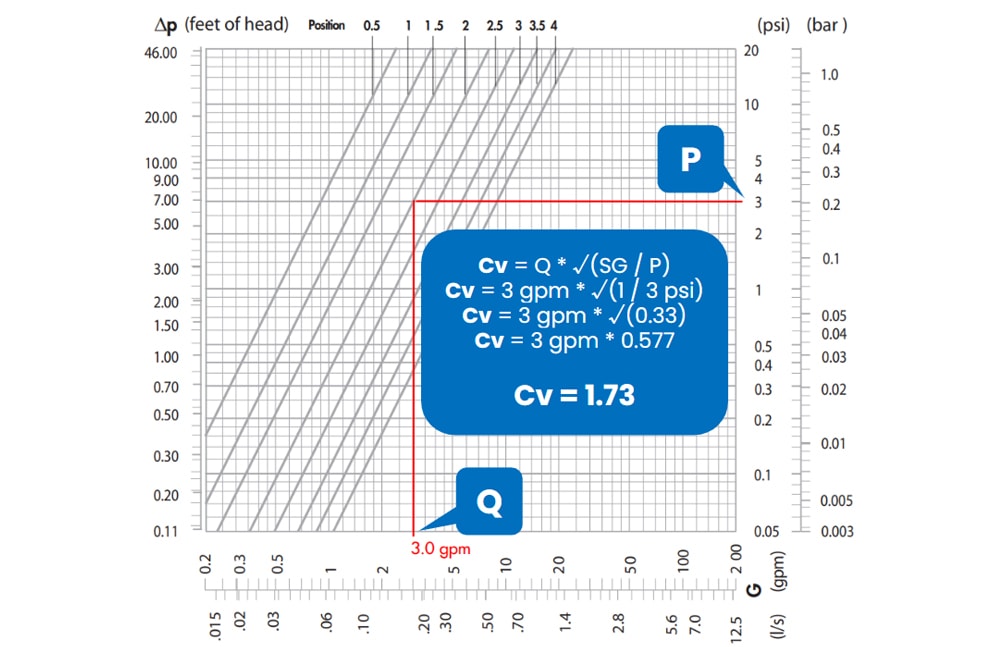
Understanding Flow Coefficient A Guide For Valve Sizing King pres sure. this should be lower than the system’s lowest pressure to ensure the valve. agm valve sizingcv value — diaphragm valves have a lower cv value than other valve types, which should be consid . ed when sizing.fluid type — due to their design, diaphragm valves are ideal for corrosive and vi. The cv of a valve, or flow coefficient, is a critical metric in understanding the efficiency and functioning of a valve within a piping system. when we define cv, it is a measure of the valve’s ability to pass fluid, denoted by the volume of the fluid that will flow per minute through the valve with a pressure drop of 1 psi. C v calculator for valve sizing. this calculator can be used to help select a valve with enough flow capacity for a given application. the valve flow coefficient (c v) is a convenient way to represent flow capacity of a valve across a range of fluids and process parameters. the c v calculator will calculate either c v or flow using the supplied. The sub critical flow is used if the upstream pressure is less than two times the downstream pressure. the cv value for gases can be found using the following formula: where: cv = valve flow coefficient. qg = gas flow in standard cubic feet per hour. t = absolute temperature in °r. (°f 460) psia = absolute pressure.
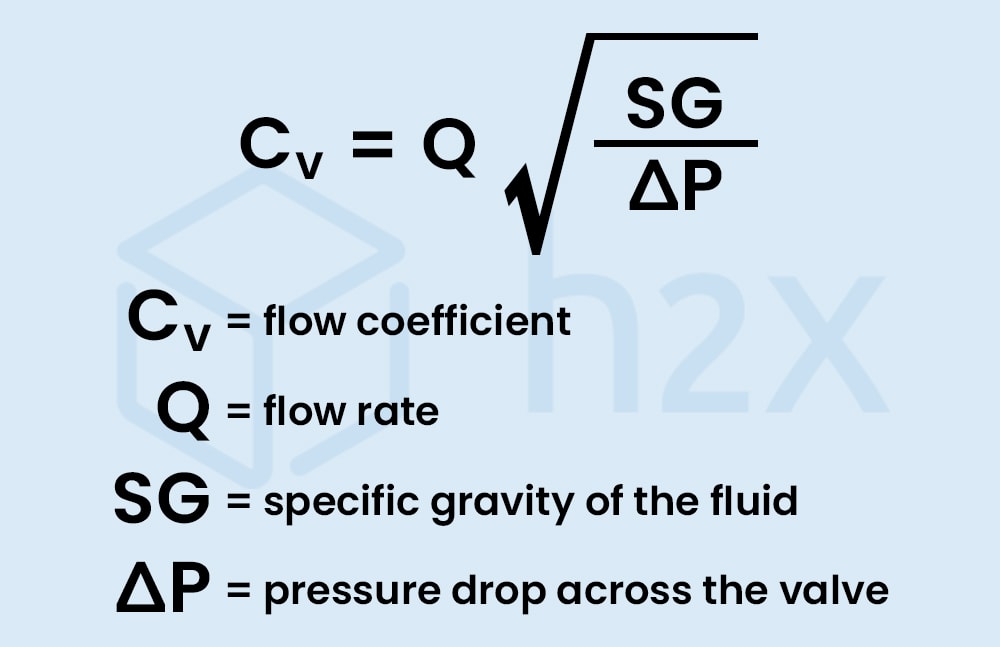
Understanding Flow Coefficient A Guide For Valve Sizing 41 Off C v calculator for valve sizing. this calculator can be used to help select a valve with enough flow capacity for a given application. the valve flow coefficient (c v) is a convenient way to represent flow capacity of a valve across a range of fluids and process parameters. the c v calculator will calculate either c v or flow using the supplied. The sub critical flow is used if the upstream pressure is less than two times the downstream pressure. the cv value for gases can be found using the following formula: where: cv = valve flow coefficient. qg = gas flow in standard cubic feet per hour. t = absolute temperature in °r. (°f 460) psia = absolute pressure. The equation used to find cv is. q = flow in gallons per minute. g = specific gravity of fluid (estimated as 1 for water systems) Δp = differential pressure over valve (delta p) – stated in psi. with this knowledge, we can quickly identify that a valve with a cv of 10 will flow 10 gpm of water at 1 psi pressure drop across the valve without. Q = cv Δ p ⁄ gf. (5 2) where q is the flow rate in u.s. gallons per minute, gf is the specific gravity of a liquid at a given temperature (water at 60°f has a gf of one), and Δp is inlet minus outlet pressure in psi. hence, one cv equals the flow of one u.s. gallon per minute of water at 60°f and under a pressure drop across the valve of.

Comments are closed.