What Is A Real Number Definition And Examples

What Is A Real Number Definition And Examples Here is the definition of a real number, a look at the sets and properties of real numbers, and specific examples of numbers that are real and imaginary. real number definition. a real number is any number that can be placed on a number line or expressed as in infinite decimal expansion. in other words, a real number is any rational or. Some of the examples of real numbers are 23, 12, 6.99, 5 2, π, and so on. in this article, we are going to discuss the definition of real numbers, the properties of real numbers and the examples of real numbers with complete explanations. table of contents: definition; set of real numbers; chart; properties of real numbers. commutative.

Real Numbers What Are Real Numbers Definitions Examples Integers include negative numbers, positive numbers, and zero. examples of real numbers: 1 2, 2 3, 0.5, √2. examples of integers: 4, 3, 0, 1, 2. the symbol that is used to denote real numbers is r. the symbol that is used to denote integers is z. every point on the number line shows a unique real number. Real numbers are closed under the arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. in other words, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of two real numbers, ‘m’ and ‘n’, always give a real number. for example, 2 5 = 7. 0.9 – 0.6 = 0.3. Real number, in mathematics, a quantity that can be expressed as an infinite decimal expansion. real numbers are used in measurements of continuously varying quantities such as size and time, in contrast to the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, …, arising from counting. the word real distinguishes them from the imaginary numbers, involving the symbol. Mathematicians also play with some special numbers that aren't real numbers. the real number line. the real number line is like a geometric line. a point is chosen on the line to be the "origin". points to the right are positive, and points to the left are negative. a distance is chosen to be "1", then whole numbers are marked off: {1,2,3.
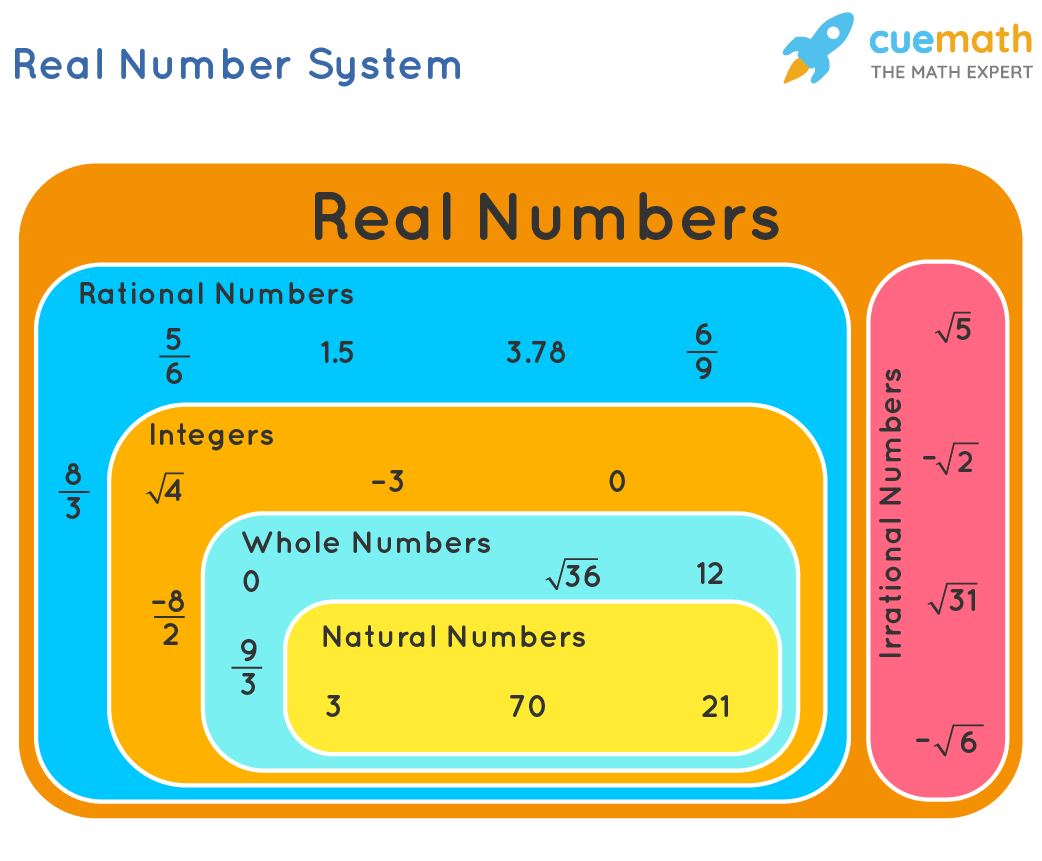
Real Numbers Definition Properties And Examples Cuemath Real number, in mathematics, a quantity that can be expressed as an infinite decimal expansion. real numbers are used in measurements of continuously varying quantities such as size and time, in contrast to the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, …, arising from counting. the word real distinguishes them from the imaginary numbers, involving the symbol. Mathematicians also play with some special numbers that aren't real numbers. the real number line. the real number line is like a geometric line. a point is chosen on the line to be the "origin". points to the right are positive, and points to the left are negative. a distance is chosen to be "1", then whole numbers are marked off: {1,2,3. In mathematics, real is used as an adjective, meaning that the underlying field is the field of the real numbers (or the real field). for example, real matrix, real polynomial and real lie algebra. the word is also used as a noun, meaning a real number (as in "the set of all reals"). Positive or negative, large or small, whole numbers, fractions or decimal numbers are all real numbers. they are called "real numbers" because they are not imaginary numbers. illustrated definition of real number: the type of number we normally use, such as 1, 15.82, minus0.1, 34, etc. positive or negative, large or small,.

Comments are closed.