What Is A Vector Definition Of Vector
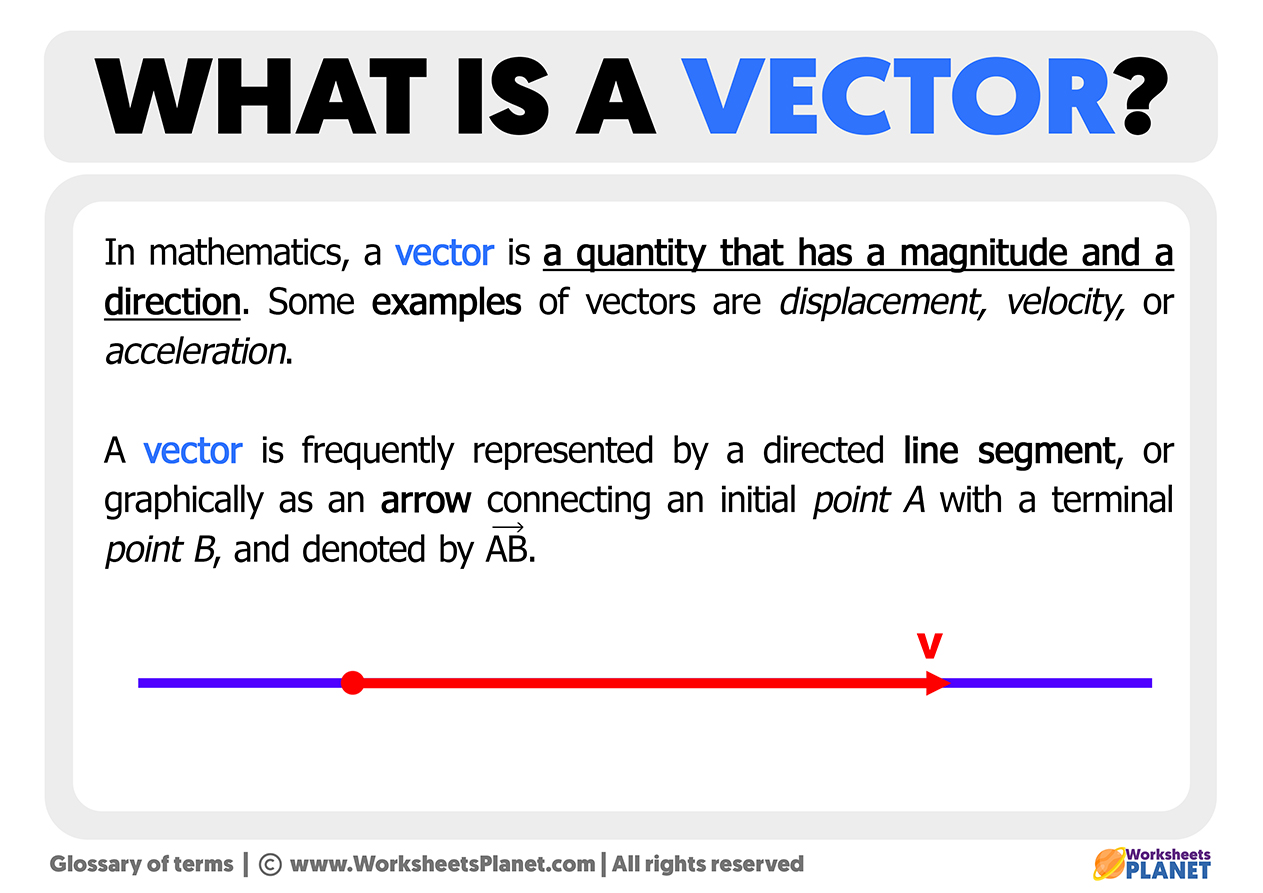
What Is A Vector Definition Of Vector In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector [1] or spatial vector [2]) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction. euclidean vectors can be added and scaled to form a vector space. a vector quantity is a vector valued physical quantity, including. A vector is a latin word that means carrier. vectors carry a point a to point b. the length of the line between the two points a and b is called the magnitude of the vector and the direction of the displacement of point a to point b is called the direction of the vector ab. vectors are also called euclidean vectors or spatial vectors.

Vector Definition At Vectorified Collection Of Vector Definition Vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. it is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude. although a vector has magnitude and direction, it does not have position. Figure 10.22: illustrating how to add vectors using the head to tail rule and parallelogram law. analytically, it is easy to see that →u →v = →v →u. figure 10.22 also gives a graphical representation of this, using gray vectors. note that the vectors →u and →v, when arranged as in the figure, form a parallelogram. Definition of a vector. a vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. the direction of the vector is from its tail to its head. two vectors are the same if they have the. A vector is formally defined as an element of a vector space. in the commonly encountered vector space r^n (i.e., euclidean n space), a vector is given by n coordinates and can be specified as (a 1,a 2, ,a n). vectors are sometimes referred to by the number of coordinates they have, so a 2 dimensional vector (x 1,x 2) is often called a two vector, an n dimensional vector is often called an n.
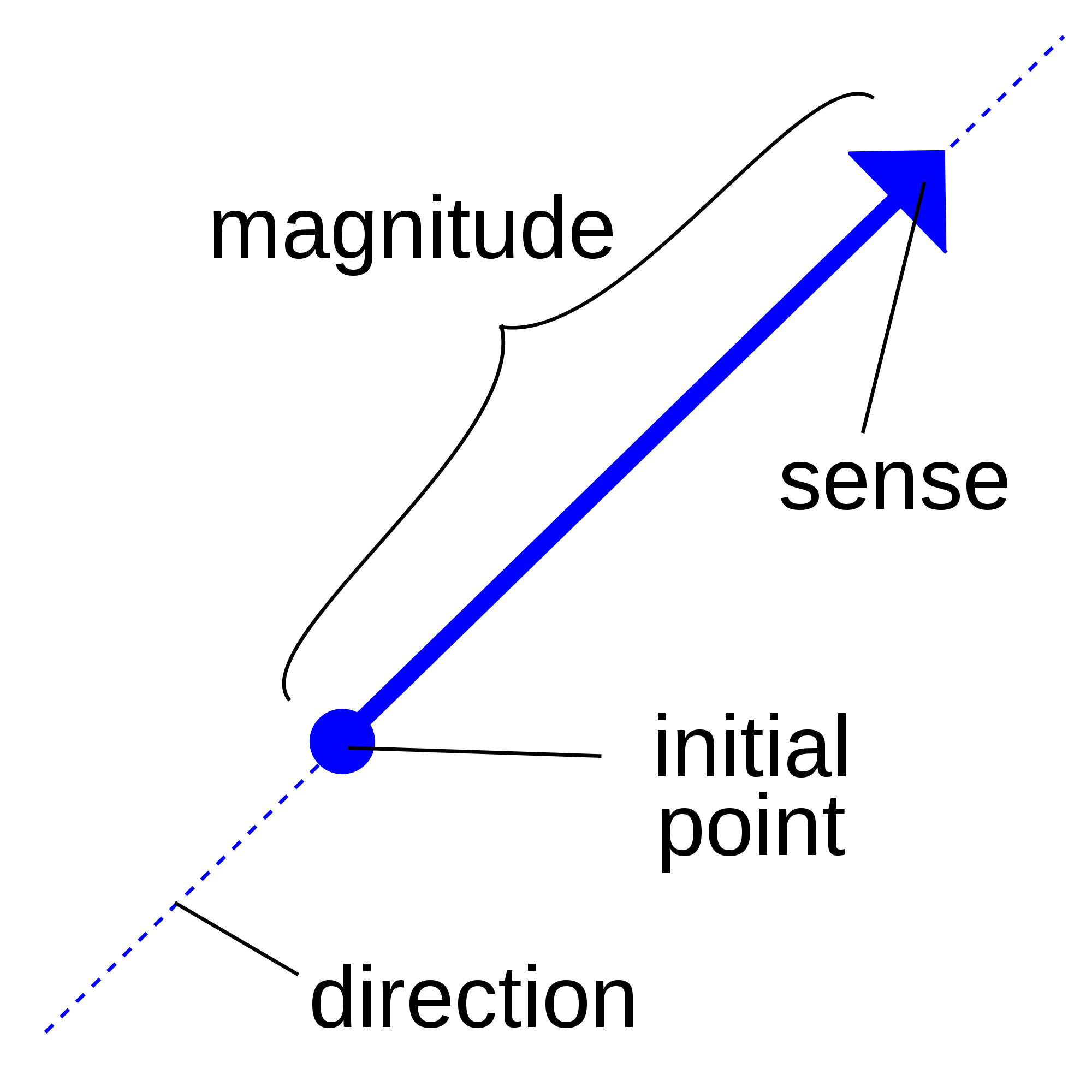
Vector Math Facts For Kids Cool Kid Facts Definition of a vector. a vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. the direction of the vector is from its tail to its head. two vectors are the same if they have the. A vector is formally defined as an element of a vector space. in the commonly encountered vector space r^n (i.e., euclidean n space), a vector is given by n coordinates and can be specified as (a 1,a 2, ,a n). vectors are sometimes referred to by the number of coordinates they have, so a 2 dimensional vector (x 1,x 2) is often called a two vector, an n dimensional vector is often called an n. A vector’s magnitude, or length, is indicated by |v|, or v, which represents a one dimensional quantity (such as an ordinary number) known as a scalar. multiplying a vector by a scalar changes the vector’s length but not its direction, except that multiplying by a negative number will reverse the direction of the vector’s arrow. for. To do so we need to turn to trigonometry. consider the figure below which depicts some vector →a with components ax and ay, →a = (ax, ay). figure 6.1.2: vector components. the magnitude (length) of the vector makes a right triangle with the two components of the vector, where the magnitude is the hypotenuse.

What Is A Vector Definition Types Video Lesson Transcript A vector’s magnitude, or length, is indicated by |v|, or v, which represents a one dimensional quantity (such as an ordinary number) known as a scalar. multiplying a vector by a scalar changes the vector’s length but not its direction, except that multiplying by a negative number will reverse the direction of the vector’s arrow. for. To do so we need to turn to trigonometry. consider the figure below which depicts some vector →a with components ax and ay, →a = (ax, ay). figure 6.1.2: vector components. the magnitude (length) of the vector makes a right triangle with the two components of the vector, where the magnitude is the hypotenuse.

Comments are closed.