What Is A Vector In Physics Definition Meaning Uses
Physics For Kids Basic Vector Math Vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. it is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude. although a vector has magnitude and direction, it does not have position. Unlock the mysteries of physics with our introductory guide, honing in on the fundamental concept of vectors. in this enlightening video, we embark on a jour.

Vector Diagram In Physics Addition Subtraction Examples Lesson We have listed the various differences between a scalar and vector in the table below: vector. scalar. definition. a physical quantity with both the magnitude and direction. a physical quantity with only magnitude. representation. a number (magnitude), direction using unit cap or arrow at the top and unit. a number (magnitude) and unit. In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector [1] or spatial vector [2]) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction. euclidean vectors can be added and scaled to form a vector space. a vector quantity is a vector valued physical quantity, including. To do so we need to turn to trigonometry. consider the figure below which depicts some vector →a with components ax and ay, →a = (ax, ay). figure 6.1.2: vector components. the magnitude (length) of the vector makes a right triangle with the two components of the vector, where the magnitude is the hypotenuse. Overview. vectors are mathematical objects represented by directed line segments, characterized by both magnitude and direction. they are often denoted by boldface letters or arrows, such as v or ab. vectors can represent various physical quantities, including displacement, velocity, force, and acceleration.

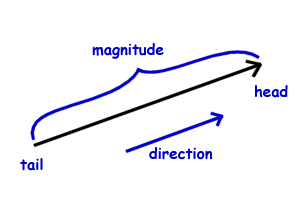
What Is A Vector Vector Magnitude Components Examples Lesson To do so we need to turn to trigonometry. consider the figure below which depicts some vector →a with components ax and ay, →a = (ax, ay). figure 6.1.2: vector components. the magnitude (length) of the vector makes a right triangle with the two components of the vector, where the magnitude is the hypotenuse. Overview. vectors are mathematical objects represented by directed line segments, characterized by both magnitude and direction. they are often denoted by boldface letters or arrows, such as v or ab. vectors can represent various physical quantities, including displacement, velocity, force, and acceleration. Most commonly in physics, vectors are used to represent displacement, velocity, and acceleration. vectors are a combination of magnitude and direction, and are drawn as arrows. the length represents the magnitude and the direction of that quantity is the direction in which the vector is pointing. Definition: vector. a vector is a quantity with both magnitude and direction. we will frequently represent a vector quantity with an arrow, where the direction of the vector is the direction that the arrow points, and the magnitude of the vector is represented by the length of the arrow. this is not to say that vectors are arrows – arrows.

Basis Vector Definition In Physics At Alan Hopper Blog Most commonly in physics, vectors are used to represent displacement, velocity, and acceleration. vectors are a combination of magnitude and direction, and are drawn as arrows. the length represents the magnitude and the direction of that quantity is the direction in which the vector is pointing. Definition: vector. a vector is a quantity with both magnitude and direction. we will frequently represent a vector quantity with an arrow, where the direction of the vector is the direction that the arrow points, and the magnitude of the vector is represented by the length of the arrow. this is not to say that vectors are arrows – arrows.

Vectors Part 1 Definition Graphical Representation Iit Jee

Comments are closed.