What Is Newtons Second Law Of Motion Physics
юааnewtonтащsюаб юааsecondюаб юааlawюаб Statement Examples And Equation Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. this verbal statement can be expressed in equation form as follows:. Newton's third law of motion. newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. this means that pushing on an object causes that object to push back against you, the same amount but in the opposite direction. for example, when you are standing on the ground, you are pushing down on the earth.

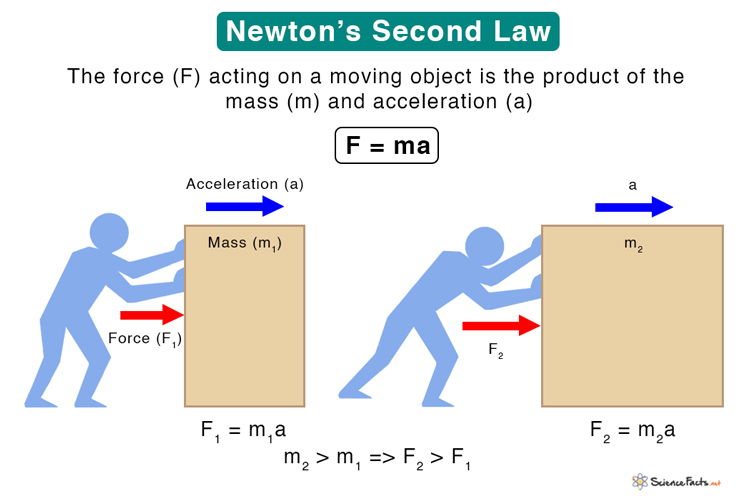
Edumission Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Newton S Second Law Of Motion Solution: newton’s 2nd law relates an object’s mass, the net force on it, and its acceleration: therefore, we can find the force as follows: fnet = ma. substituting the values, we get. 1000 kg × 4 m s 2 = 4000 n. therefore, the horizontal net force is required to accelerate a 1000 kg car at 4 m s 2 is 4000 n. What is newton's second law? (article) | khan academy. physics archive. course: physics archive > unit 3. lesson 1: newton's laws of motion. newton's first law of motion introduction. Newton's first law expresses the principle of inertia: the natural behavior of a body is to move in a straight line at constant speed. a body's motion preserves the status quo, but external forces can perturb this. the modern understanding of newton's first law is that no inertial observer is privileged over any other. This type of motion is addressed by newton’s second law of motion, which states how force causes changes in motion. newton’s second law of motion is used to calculate what happens in situations involving forces and motion, and it shows the mathematical relationship between force, mass , and acceleration .

Newton S Second Law Of Motion Overview Video Physics Ck 12 Newton's first law expresses the principle of inertia: the natural behavior of a body is to move in a straight line at constant speed. a body's motion preserves the status quo, but external forces can perturb this. the modern understanding of newton's first law is that no inertial observer is privileged over any other. This type of motion is addressed by newton’s second law of motion, which states how force causes changes in motion. newton’s second law of motion is used to calculate what happens in situations involving forces and motion, and it shows the mathematical relationship between force, mass , and acceleration . Newton’s second law of motion. the acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system and is inversely proportion to its mass. in equation form, newton’s second law is \[\vec{a} = \frac{\vec{f} {net}}{m},\]. Newton’s second law is one of the most important in all of physics. for a body whose mass m is constant, it can be written in the form f = ma, where f (force) and a (acceleration) are both vector quantities. if a body has a net force acting on it, it is accelerated in accordance with the equation. conversely, if a body is not accelerated.

Comments are closed.