What Triggered The Big Bang How The Universe Works

What Triggered The Big Bang How The Universe Works Youtube The big bang is one of science's most famous theories, but we now know it wasn't big and it wasn't a bang.stream full episodes of how the universe works:http. Burn that sentence into your brain. say it before you go to sleep, and first thing when you wake up. the big bang theory is a model of the history of the universe, tracing the evolution of the.
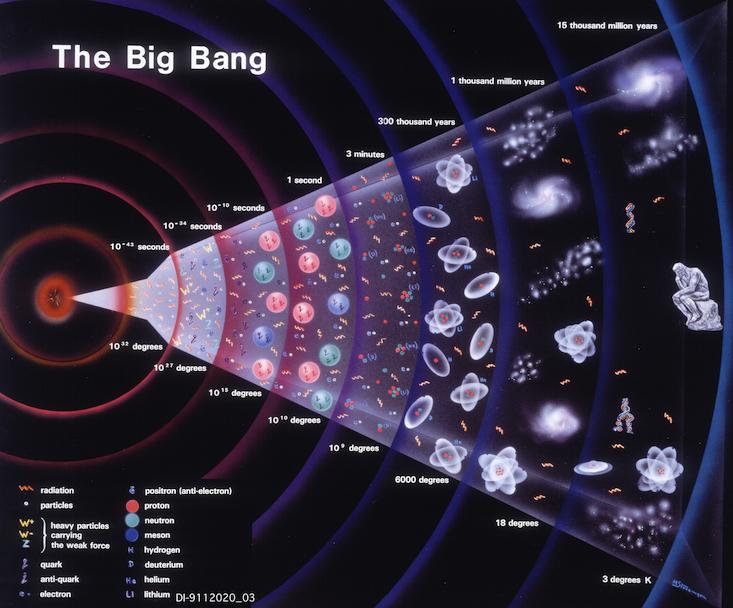
The Tangled History Of Big Bang Science Nautilus Science Connected Step 2: the universe's first growth spurt. step 3: too hot to shine. step 4: let there be light. step 5: emerging from the cosmic dark ages. step 6: more stars and more galaxies. step 7: birth of. The universe cooled rapidly as it blew outward, however, and by 10–35 second after the big bang, the epoch of inflation occurred, enlarging the universe by a factor of 1050 in only 10–34. Overview. the origin, evolution, and nature of the universe have fascinated and confounded humankind for centuries. new ideas and major discoveries made during the 20th century transformed cosmology – the term for the way we conceptualize and study the universe – although much remains unknown. learn more. The big bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. [1] the notion of an expanding universe was first scientifically originated by physicist alexander friedmann in 1922 with the mathematical derivation of the friedmann equations. [2][3][4][5].

Big Bang Theory Our Universe The Beginning Of The Space Time Overview. the origin, evolution, and nature of the universe have fascinated and confounded humankind for centuries. new ideas and major discoveries made during the 20th century transformed cosmology – the term for the way we conceptualize and study the universe – although much remains unknown. learn more. The big bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. [1] the notion of an expanding universe was first scientifically originated by physicist alexander friedmann in 1922 with the mathematical derivation of the friedmann equations. [2][3][4][5]. Most physicists believe the universe was born in a big bang 13.8 billion years ago. in it, the energy making up everything in the cosmos we see today was squeezed inside an inconceivably small space – far tinier than a grain of sand, or even an atom. then, this unimaginably hot and dense cauldron – for whatever reason – ballooned at a. About 13.8 billion years ago, the universe sprang into existence in an event known as the big bang. the early universe was incredibly hot — too hot for even atoms to exist — and extraordinarily dense. as the universe expanded, its temperature and density decreased. atoms formed, then molecules. gravity drew the matter into greater and.

Comments are closed.