X Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Xps Basic
X Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Xps Chemistry Libretexts X ray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps) has become one of the most widely used surface analysis techniques, and xps instrumentation has become more user friendly, making the technique available to a large number of researchers. the number of experts in the field, however, has not increased, and xps data are often misinterpreted in the literature. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy. basic components of a monochromatic xps system. x ray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps) is a surface sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the very topmost 200 atoms, 0.01 um, 10 nm of any surface. it belongs to the family of photoemission spectroscopies in which electron population.
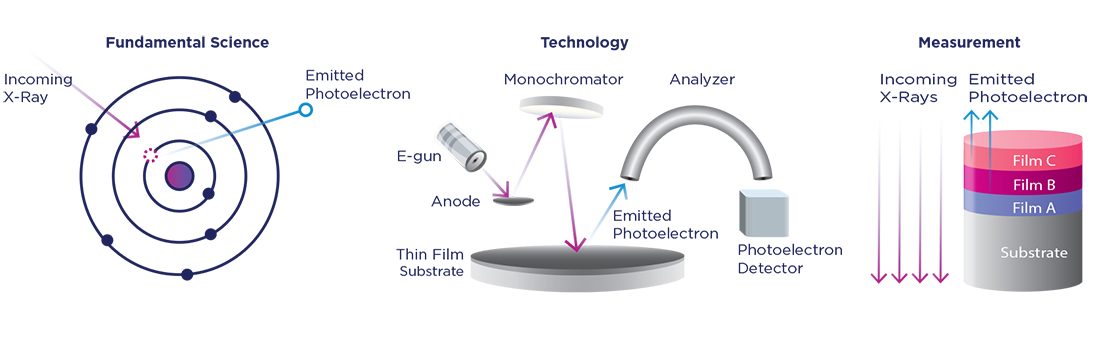
X Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Xps Nova History of x ray photoelectron spectroscopy basic principles behind xps resources – instruments, people, software and information sample types, sizes and how they are put into xps instruments an example – basic spectral features how a simple quantification works more spectral features peak shapes: single peaks, doublets, and extra complexity. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps) has become one of the most widely used surface analysis techniques, and xps instrumentation has become more user friendly, making the technique available to a large number of researchers. the number of experts in the field, however, has not increased, and xps data are often misinterpreted in the literature. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy principle. the characteristic binding energies of core electrons in atoms keep them in their orbitals. the characteristics of adjacent atoms, orbital kinds, and atom types all influence the binding energies. the binding energies of electrons emitted from the sample surface are measured by xps. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps), also known as electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (esca), is used to determine quantitative atomic composition and chemistry. a sample is irradiated with monochromatic x rays, resulting in the emission of photoelectrons whose energies are characteristic of the elements within the sampling volume.

Xray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Xps Www Nano 4 Me X ray photoelectron spectroscopy principle. the characteristic binding energies of core electrons in atoms keep them in their orbitals. the characteristics of adjacent atoms, orbital kinds, and atom types all influence the binding energies. the binding energies of electrons emitted from the sample surface are measured by xps. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps), also known as electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (esca), is used to determine quantitative atomic composition and chemistry. a sample is irradiated with monochromatic x rays, resulting in the emission of photoelectrons whose energies are characteristic of the elements within the sampling volume. Xray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps) is one of the foremost tools for studying this surface chemistry. in its simplest form, xps involves shining xrays onto a material to knock electrons from the surface atoms. by counting these ejected electrons and measuring their energy, it is possible to. Over the past three decades, the use of x ray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps) has grown and it is now the most commonly applied method of surface analysis. 5 xps has become essential for many types of research, expanding from chemistry and materials science into many other areas including those associated with environmental, 6, 7 atmospheric.
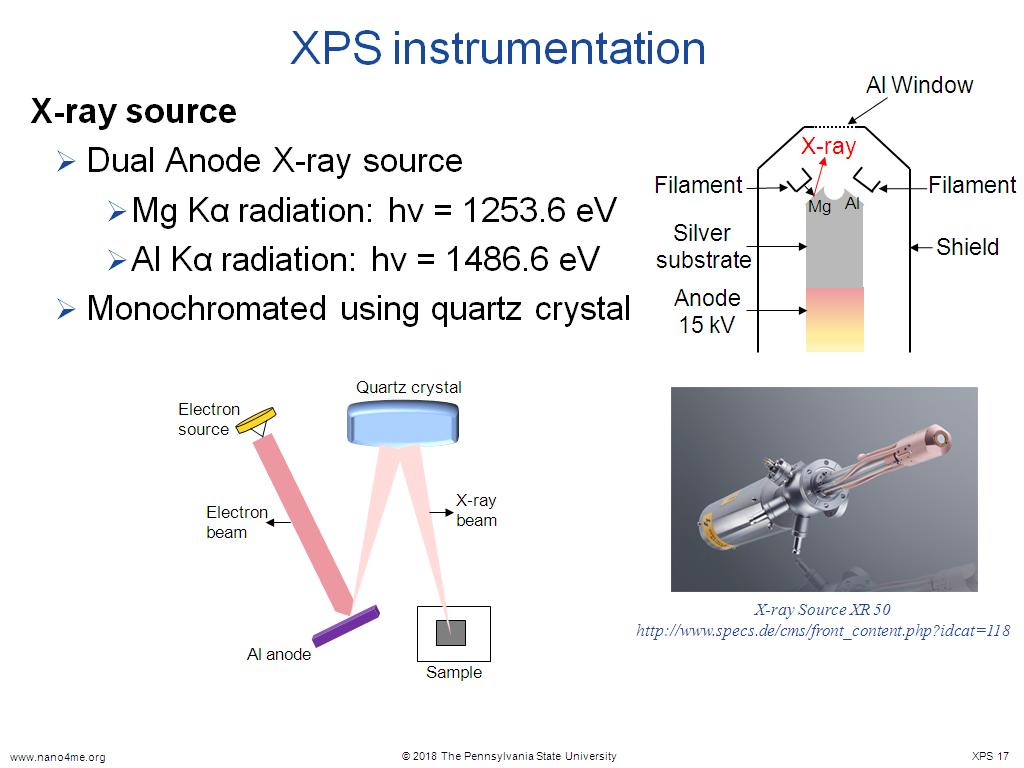
Nanohub Org Resources X Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Xps Watch Xray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps) is one of the foremost tools for studying this surface chemistry. in its simplest form, xps involves shining xrays onto a material to knock electrons from the surface atoms. by counting these ejected electrons and measuring their energy, it is possible to. Over the past three decades, the use of x ray photoelectron spectroscopy (xps) has grown and it is now the most commonly applied method of surface analysis. 5 xps has become essential for many types of research, expanding from chemistry and materials science into many other areas including those associated with environmental, 6, 7 atmospheric.

X Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Xps Analysis A Full Scan Spectrum

Comments are closed.