Your Quick Easy Guide To Manual Handling

Manual Handling Top 10 Tips Infographic Key takeaways. muscoskeletal disorder is very common in construction. the main cause is manual handling. especially manual handling done badly. watch out for repetitive movements, and movement that requires great bodily force. choose lighter materials, prepare in advance so lifting will be avoided, use mechanical aids. Manual handling is an activity of transporting or supporting a load including lifting, pushing, pulling, carrying, throwing, and moving objects by hand or bodily force. it is a common practice in different industries such as manufacturing, construction, agriculture, and more.
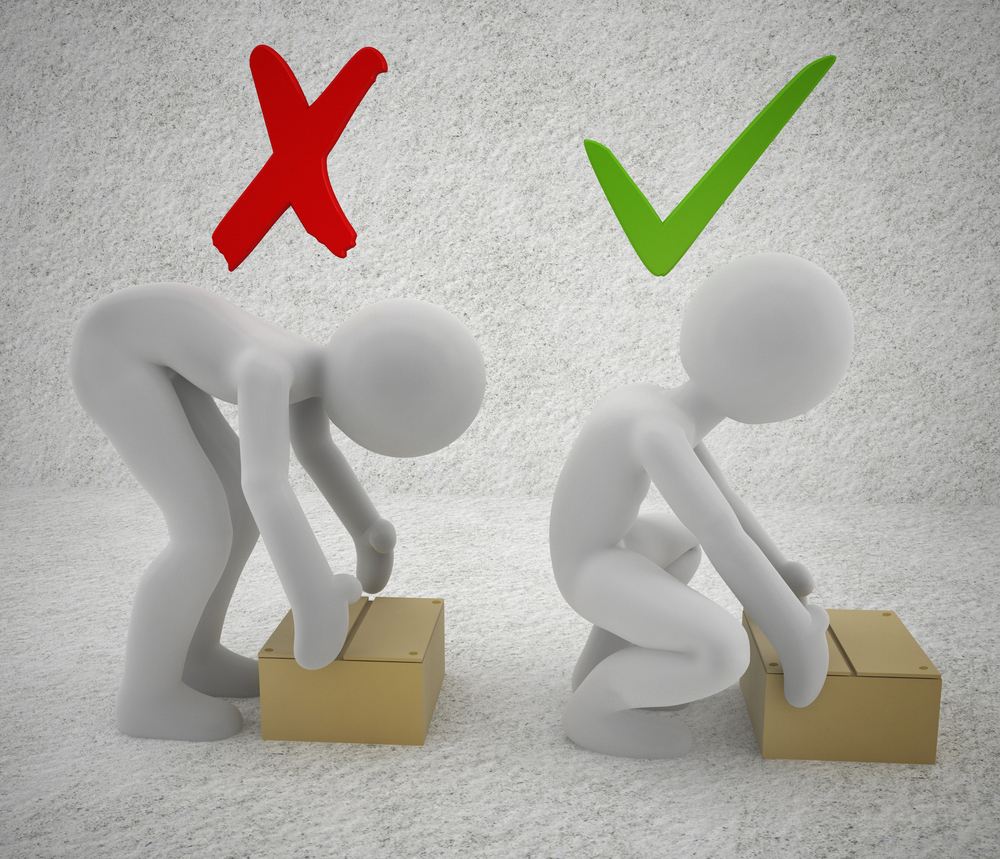
Your Quick Easy Guide To Manual Handling Incorrect manual handling can lead to a wide range of injuries and health problems, especially msds. this can have a serious impact on an individual's health and well being. proper manual handling can help prevent msds, as well as other injuries that may arise due to incorrect techniques. efficiency & productivity. Center your body and feet correctly, keeping your feet apart for maximum stability. avoid twisting and do not bend your back or lean forward. awkward posture or incorrect positioning can increase the risk of musculoskeletal injury and put excess stress on your back. To achieve good manual handling techniques, follow these 7 basic principles when dealing with basic lifting, pushing, pulling, lowering, filling, emptying, or carrying: ensure the object is light enough to lift, steady, and unlikely to shift or move. remove obstructions ensure your route is clear and there is space to lower the load wherever. According to the health and safety executive (hse), manual handling causes over a third of all workplace injuries, including musculoskeletal disorders (msds), such as back pain, sprains, strains, and hernias. manual handling also accounts for a large proportion of work related ill health, absenteeism, and reduced productivity 2.

Comments are closed.